In the wide world of Linux, learning simple yet powerful commands is key to becoming a proficient user. One such essential skill is appending lines to a file, a fundamental operation for adding information or modifying configurations.
In Linux, text files store information in plain text, and each line typically represents a piece of data. Appending lines involves adding new information to the end of an existing file, preserving its current content.
In this tutorial, we’ll explore several commands for adding one or more lines to a file, expanding your understanding of file manipulation in the Linux environment.
1. echo Command
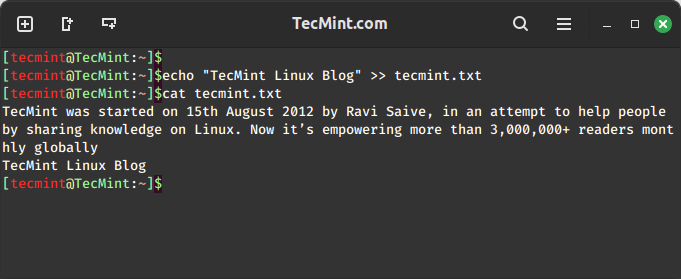
The echo command is a simple yet powerful tool that is used to append lines to a file using the >> operator as shown.
echo "TecMint Linux Blog" >> tecmint.txt
This command appends the specified text to the end of the file named “tecmint.txt“. If the file doesn’t exist, it will create it.
2. printf Command
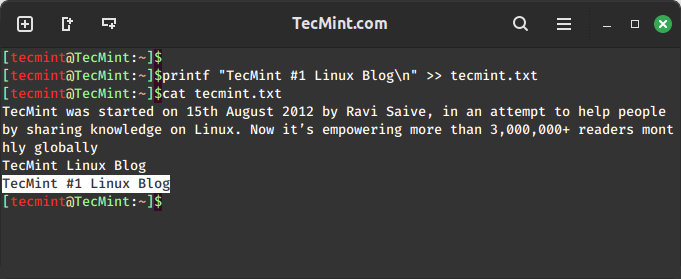
Another option is the ‘printf‘ command, which offers more formatting options compared to ‘echo‘.
To append lines, follow a similar structure:
printf "TecMint #1 Linux Blog\n" >> tecmint.txt
The '\n' represents a newline character, ensuring that the new content appears on a new line in the file.
3. tee Command
The tee command not only appends lines to a file but also allows interactive input, which can be particularly handy for situations where you want to input multiple lines manually.
tee -a tecmint.txt
After running this command, any text you type will be appended to the specified file.
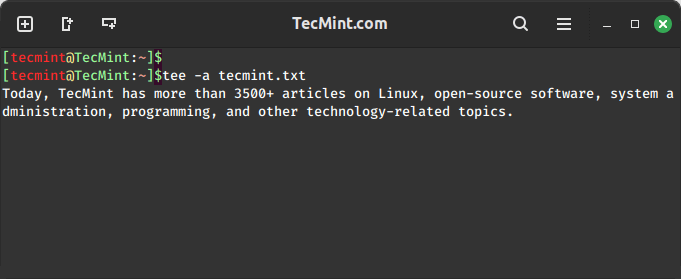
Press 'Ctrl + D' to exit and save the changes.
4. cat Command
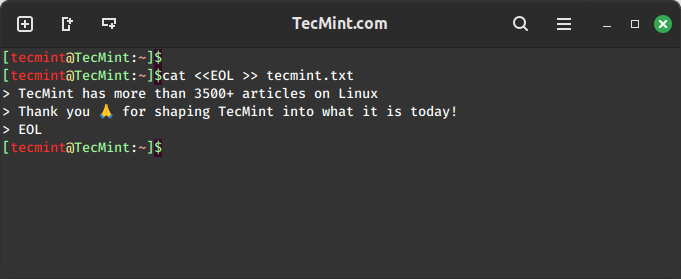
The cat command, commonly used to concatenate and display file content, can also append lines using a here document.
cat <<EOL >> tecmint.txt New line of information 1 New line of information 2 EOL
This method is beneficial when you need to append multiple lines at once.
Conclusion
Adding lines to a file in Linux is crucial, which lets you tweak settings, add new info, or store data by using commands like ‘echo‘, ‘printf‘, ‘tee‘, and ‘cat‘ make it easy, especially for beginners.
By understanding and practicing these commands, users can confidently navigate and manipulate files, unlocking the full potential of the Linux command line.
As you continue your Linux journey, remember that each command is a building block, and mastering them will enhance your overall proficiency and efficiency in managing your system.





Nice little tricks provided. Thanks, I was unaware of
tee -acommand.